The ‘Dirty Quid Pro Quo’ Between Democrats and Big Tech
Briahna Joy Gray, former 2020 Sanders Campaign National Press Secretary, recently delivered a commentary on The Hill’s Rising about two significant bills regarding social media censorship. One, from Texas, blocked by an emergency order of the U.S. Supreme Court, would ban social media companies from removing posts based on the views they express. The case is pending in federal appeals court and may return to the Supreme Court. The other was a Florida law, in which a preliminary injunction was upheld by the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals that would have prohibited social-media companies from “deplatforming” political candidates, from prioritizing or deprioritizing any post in the algorithm “by or about” a candidate, and from removing anything posted by a “journalistic enterprise” based on its content.
Gray claimed that if the Texas bill, HB20, had passed, “social media freedoms would have been seriously curtailed.” She described the Supreme Court justices who dissented from the bill as “anti-speech,” and suggests that the moderation social media platforms utilize (banning users, algorithmic deprioritization, suppression of news stories, etc.) are a part of their First Amendment rights. In the case of the Florida bill, Gray claimed that Republican lawmakers “couldn’t care less” about the First Amendment rights of these companies.
Knowing that the Supreme Court has ruled that corporations do have First Amendment rights and that the First Amendment does not limit private businesses, Gray’s characterization of the bills’ advocates as anti-speech and the 11th Circuit Court of Appeal’s ruling that “these platforms are private actors,” may appear totally sound. But they are not. Whether or not these platforms have free speech is not the issue. The reason Google and social media companies are even allowed to exist is because of Section 230 of the Decency Act, which defined them as public utilities, acting as neutral providers. This is why they cannot be sued for libel. They are not meant to be editors, but providers of a service; expecting them to editorialize changes the very function of the duty that they are meant to fulfill.
Can Today’s Social Media Platforms Really Be Described as “Neutral Providers?”
These social media companies have abandoned their “neutral” position as “public utilities” and instead embraced the advantages of being private entities in corporate America. To this end, it’s instructive to examine how Big Tech giants have wielded their censorious powers and to which political actors they’ve donated boatloads of money.
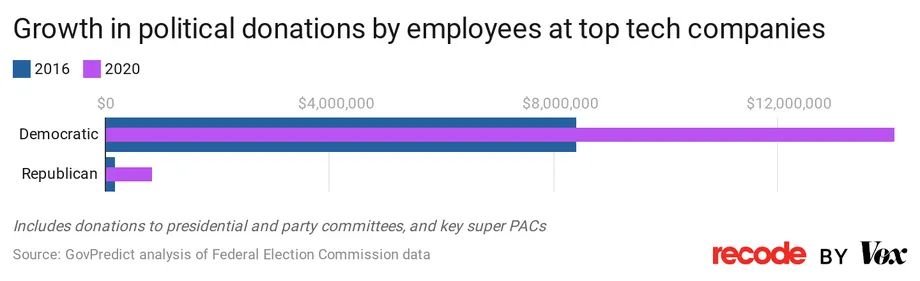
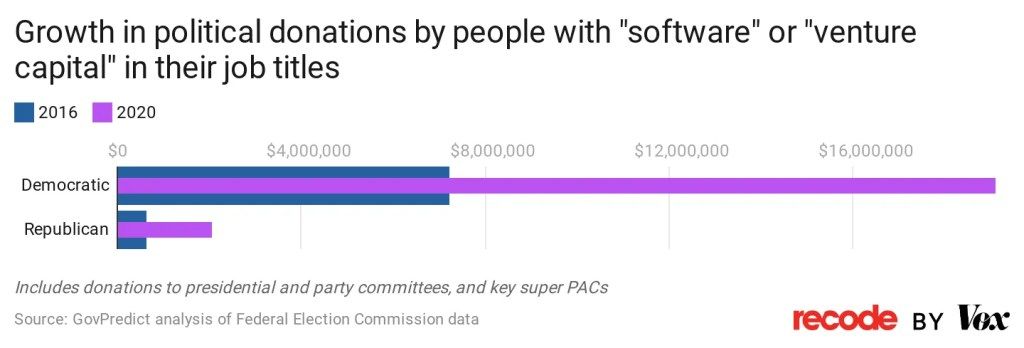
The appeals court that upheld the preliminary injunction against the Florida law claimed that the right for platforms to curate speech as they see fit, free of government mandates, “develops particular market niches, fosters different sorts of online communities, and promote[s] various values and viewpoints.”
The court must have forgotten that we can see, just by looking at how these platforms have curated speech in the past, that this claim is nothing but pure fantasy. The censorship of those who challenged the mainstream narrative on the Bucha incident in Ukraine, dissenting voices on vaccine policy/efficacy, ANTIFA groups on Twitter, the left-wing podcast ChapoTraphouse on Reddit, #StoptheSteal advocates, the now verifiably real Hunter Biden laptop story, and all of Russian media on YouTube — proves Big Tech censorship has only worked to narrow the discourse of the most important political events of our time in a pro-establishment, anti-dissent direction.
More important, Big Tech’s content moderation most often seems to align with the Democratic Party establishment narrative. This is especially apparent in the censorship of the Hunter Biden laptop story, which Twitter claimed without evidence that the New York Post acquired using “hacked materials.” When we look at how Silicon Valley has financially invested in the Democrats with dark money, the intent of their censorship becomes more clear. Facebook’s top executives have donated at least $3.9 million to political campaigns, including $220,000 to Joe Biden’s 2020 presidential campaign alone. Its former COO Sheryl Sandberg gave $416,000 to a committee supporting Hillary’s 2016 run in addition to $405,000 to the PAC for Emily’s List, backing pro-chocie Democrats. In the 2022 cycle alone, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation has doled out $332,706 in political contributions, and spent $1,760,528 in 2020, the vast majority of which went to Democrats both years. In 2020, of the $815,549 Twitter spent on federal candidates, 98% went to Democrats. This is, according to Pulitzer-Prize winner Chris Hedges, “a part of a dirty quid pro” in which Big Tech censors Democratic Party critics and in return the Democrats won’t touch their monopolies.
Even more incriminating, Big Tech CEOs have openly stated their biases in censorship, such as when the YouTube CEO, Susan Wojcicki, stated that the platform uses separate algorithms for independent news and “authoritative sources.” Arguably the most striking admission came from YouTube executive Neal Mohan who openly stated, “…community guidelines are derived from either established third party experts that we work with whether it’s around hate speech or harassment, violent extremism, where we work with government authorities…child safety where we work with child advocacy and government groups.”
These companies have become so similar to the other giant corporations that have bought out government in their monopolization, funding of government, and political agendas that they have completely abandoned the role that Section 230 of the Decency Act gave them: neutral providers.
The Contradictions of the Courts
However, none of this debunks the argument that the courts are making a principled decision by upholding the previous rulings of the Supreme Court that corporations do have First Amendment rights and that the First Amendment does not limit private businesses. If they believe that corporations’ and private businesses’ rights to freedom of expression are essential to protecting freedom of speech, then one could argue these rulings are reasonable despite the legalized corruption between the Democrats and Big Tech.
It becomes hard to believe any principled action was taken, however, knowing that neither the Supreme Court, nor any circuit court of appeals, took action to block or uphold a preliminary injunction against Democratic Senator Anna Kaplan’s recent New York law, Senate Bill S4511A, which “requires social media networks to provide and maintain mechanisms for reporting hateful conduct on their platform.”
The legislation defines hateful conduct, or hate speech, as: “the use of a social media network to vilify, humiliate, or incite violence against a group, or a class of persons on the basis of race, color, religion, ethnicity, national origin, disability, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity or gender expression.”
This is a clever way of wording the legislation because, as most would agree, it is wrong to vilify, humiliate, or incite violence against any group. This makes the effort to censor these actions appear reasonable, even humane. The disingenuity of this framing, though, stems from the fact that once the ability to censor under these conditions is granted, the powerful then use these guidelines to censor anyone who poses a threat to power. Because there is no specific way to define what is “vilifying, humiliating, or inciting violence against a group,” giving any powerful institution the ability to censor under these contexts only grants them free range to censor as they please – most often in their favor.
This can be seen in YouTube’s censorship of The Grayzone’s Max Blumenthal and Aaron Maté’s discussion of Paul Mason’s collusion with U.K. intelligence to deplatform The Grayzone. YouTube claimed the video had been “removed for violating YouTube’s policy on harassment and bullying,” without any explanation as to what constituted either harassment or bullying in the video.
This abuse of power is even clearer in how social media companies have censored Palestinian rights advocates. Facebook censored Palestinian voices by inaccurately labeling their use of words such as “martyr” and “resistance” as an incitement of violence. In 2021, Facebook and Instagram labeled Jerusalem’s Al-Asqa Mosque—the third holiest site in Islam—as being connected to “violence or a terrorist organization.” This then resulted in Instagram taking down posts that had the hashtag #AlAqsa.
ScheerPost’s own Patrick Lawrence was permanently suspended from Twitter for “abusive behavior” without any indication of how he engaged in such behavior.
Granting these tech platforms the ability to censor under these provisions, or in the case of New York Senate Bill S4511A actually requiring that they censor under these guidelines, gives these companies the ability to label any inconvenient discussion as the kind of speech they wish to censor. Whether it be hate speech, harassment, or something else, those who challenge the mainstream narratives disseminated by the powerful will likely find themselves the victims of censorship and erasure.
According to Senator Kaplan’s communication director, Sean Ross Collins-Sweeney, Senate Bill S4511A is “different” than the censorship bills from Florida and Texas since “It does not infringe on First Amendment rights because it does not say what can or cannot be on a platform.”
Collins-Sweeney made this statement despite the fact that the bill includes a definition of hate speech, and enforces its requiring of these companies to report hate speech by “assess[ing] [any social media platform that knowingly fails to comply with these requirements] a civil penalty of not more than $1,000 per day.” Despite these clear contradictions, the courts have taken no action to block this bill from passing.
The Solution
Are the Florida and Texas bills, which would surely limit the censorship ability of these Big Tech giants, the solution to corporate censorship? Probably not. These monopolies would ultimately still exist, and still possess their egregious financial power. In a system where both parties are corrupted by corporate money, that means the Silicon Valley kingpins can always just buy influence over the Republican Party, too, and impose censorship for them instead.
To label attempts at restricting the censorship power of these companies—for political reasons or not—as anti-speech, or describing the striking down of these bills as a First Amendment victory, is naive at best and dishonest at worst. While these bills are almost definitely not a permanent solution, they would work to take power away from these tech giants and the Democratic party, and give some power (through freedom of expression) back to the citizens of the internet.
As cooperation between Big Tech and the government increases, and the courts’ favoring of censorship becomes more apparent, it becomes clear what is required that we live in a functioning democracy. Unless we make these companies what they were supposed to be since their conception—public utilities acting as neutral providers—we have no chance of maintaining the First Amendment rights that the country was founded upon.











